The Cosmos Stack Roadmap for 2026

Earning the right to scale, and scaling:
An updated roadmap focused on performance, improving modularity, and enterprise-focused features.
Cosmos Lab's engineering team is excited to share the Cosmos Stack Roadmap through Q3 2026, recapitulating our work this last year as well.
This article covers major upgrades launched in 2025 and dives deeper into the exciting work that is coming next. Now that we have a year of core stack development under our belt, we’re hopeful that we’ll be able to accelerate and increase our output next year.
The 25-26 period reflects a simple guiding principle: earning the right to scale, and then scaling. In short, we’ve made the necessary work to scale, and now are working to make major improvements to performance (throughput, blocktime, and stability under load), interoperability, and core functionality for enterprises (proof-of-authority, privacy).
- On performance, we’re already running multiple experiments across IAVL, the mempool, and networking layer that are showing a ton of promise. We have doubled our TPS on our internal network, latency is improved, and for the first time ever, our internal test networks aren’t falling over under massive p2p loads.
- On connectivity, we’re close to productionizing IBC v2 light clients for Solana and a general solution that will work across all EVM/L2 chains. In 2025, we added Ethereum to the IBC network. In 2026, we think this work will allow us to add dozens of networks.
- On enterprise functionality, we’ve developed a PoC of a Proof-of-Authority (PoA) solution that doesn’t require forking the Cosmos SDK or launching a “stake” token; and are researching flexible privacy solutions to integrate onto the stack.
Contribute. Connect. Support.
Whether you are a team or business using the stack, or a contributor, auditor, or researcher, this roadmap lays out the key improvements we aim to deliver in the coming year. Join us:
- For contributing, visit our GitHub organization & our contributors Slack channel
- For performance discussions, join the performance working group
What We Shipped in 2025

In 2025, Cosmos Labs brought the development of the Cosmos Stack fully back in-house, with the Interchain Foundation, and started a grand overhaul and sanitization of all components.
Onboarding quickly surfaced a set of systemic constraints. Unnecessary complexity and fragmented coordination. After talking to stack users, our priorities were clear: for the stack to be ready for growth, we had to: make the Cosmos SDK much easier to upgrade; simplify IBC to allow the protocol to be implemented anywhere; add support for a native EVM framework, in high-demand. As a result, we launched:
- v0.53 of Cosmos SDK: This release introduced new features without breaking existing functionalities, ensuring a seamless upgrade path for our users. We were able to deliver an SDK upgrade that constituted 2 lines of code changed (excluding linter comments) live in many major chains like Babylon, MANTRA, Cosmos Hub, Warden, and Crypto.com.
As the heart of the stack, this foundational change allows us to bring all other component upgrades to the SDK seamlessly, and fast, without breaks.
- v10 of ibc-go & IBC v2: We released a significant improvement of the IBC protocol itself: IBC v2, which simplifies the protocol by removing channel and connection handshakes, reducing complexity and enabling easier implementation in other ecosystems and VMs. In this release, we also included the first stable release of 08-wasm and the callbacks middleware.
- IBC Solidity and CosmWasm Ethereum light client: With IBC v2 we were able to implement IBC in Solidity, paving the way for IBC to make its way to Ethereum.
With this, and our work on attestation, IBC can now finally be expanded anywhere, starting with Ethereum, and next Solana, L2s, and any other network.
- Initial Versions of the Cosmos EVM: We acquired, open-sourced, and further developed Cosmos EVM. Our focus for the Cosmos EVM has been on security, performance, and providing a truly native EVM experience. Chains using it already include Ripple, Mezo, KiiChain, Telegram/TAC, Mantra and more.
- Security Audited Release - v0.4.0: Delivered critical security fixes and introduces a true EVM mempool, enabling full compatibility with popular tools like Forge.
- Bug Bounty Coverage - v0.5.0: Added native account abstraction in the EVM via EIP-7702, simplifying user interactions.
Today, we are excited to report that the Stack team is operating as a single end-to-end unit, accelerating release cycles across all components. In 2025, we walked and set new foundations in stack development, dependencies, and security, so that in 2026 we could run.
Thanks to these learnings, and investments, we can now rapidly accelerate innovation and performance improvements on the stack, aligned with the needs of enterprise customers.
Future Improvements to the Cosmos Stack

With the groundwork done, in 2026 we will accelerate on scaling the stack. By the end of this year, we want the stack at its best in performance, connectivity, experience, and onboarding a new set of key enterprise features.
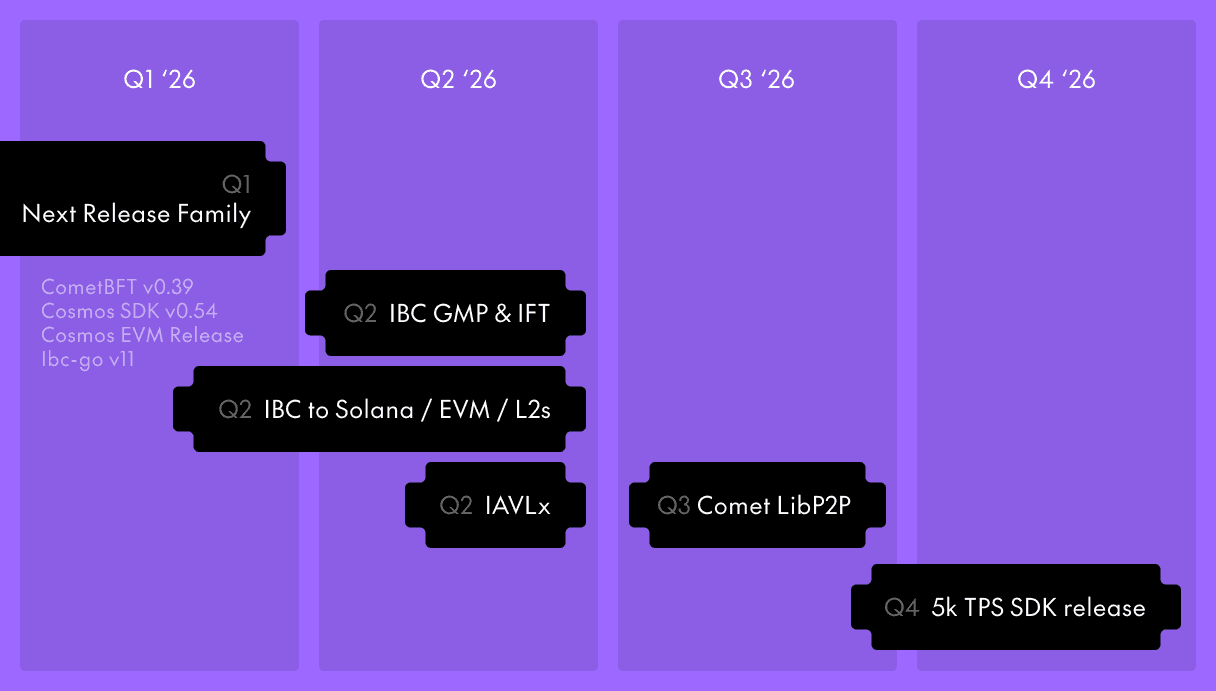
Here is our projection for the major milestones ahead:
- End of Q1 / Early Q2 — Next release family (CometBFT v0.39, Cosmos SDK v0.54, ibc-go v11) with native Proof of Authority, BLS signing, and BlockSTM
- Q2 — IBC GMP, IFT, Solana and L2/EVM support, and IAVLx storage rewrite
- Q3 — CometBFT libp2p networking target for production
- Q4 — SDK release targeting 5,000 TPS & 500ms blocktimes sustained in production
For that, we sowed the seeds of our 2025 R&D work, and began productizing key innovations and improvements across all areas of the stack. You can find a detailed breakdown of all upcoming improvements, and their background, below.
Performance

Cosmos is widely recognized as the most battle-tested blockchain stack in production. Over the past seven years, more than 200 chains have been built using Cosmos—more than any other ecosystem. This adoption gives us a strong foundation, and a clear opportunity to lead on performance.
Today, performance is our highest priority. Internally, we treat this as a code-red focus area to ensure Cosmos remains a platform of choice for global, consumer-grade financial applications – where throughput, latency, and reliability under load are essential. As expectations continue to rise across the industry, Cosmos must not only remain competitive on speed to stay competitive, but lead in the research and systems engineering required to operate at global scale.
To do that, the stack must deliver predictable performance under the network configurations most new chains actually use: 10–25 geographically distributed validators. This means materially increasing throughput, reducing block times, and maintaining stability under sustained and adversarial load.
Our first global-scale performance targets are:
- 5,000 TPS in sustained production
- 500ms block times
- Stable performance under load, including sophisticated DDoS scenarios
These targets are about production reality, not benchmarks. Our goal is to make this level of performance the default across real Cosmos networks using standard configurations. By optimizing every layer of the stack end to end, we believe this is achievable in 2026.
This work is difficult and iterative. The Cosmos stack is mature and complex, which is why meaningful gains require careful experimentation rather than starting over. Several high-impact efforts are already underway, including making ABCI fully concurrent and a full rewrite of IAVL.
Performance at this scale benefits most from close ecosystem collaboration. Our partnerships with teams like Cronos and MANTRA have already proven highly effective, and we plan to expand this model with additional Cosmos Stack users or contributors!
Contribute to the Cosmos Performance Working Group:
We’re excited to expand our performance efforts by forming a Cosmos Performance Working Group. Anyone interested in participating is encouraged to reach out HERE.
Cosmos SDK and Cosmos EVM
Execution Layer - BlockSTM:
We will be integrating BlockSTM to significantly boost transaction processing capabilities via graph parallelism, as demonstrated by early successes by Cronos.
We’ve integrated and reproduced the results of performance improvements introduced with BlockSTM. In terms of average transaction processing throughput introduced (shown below on a small scale load test pushing around 400 transactions per second) there is a clear increase in the rate at which the SDK can process transactions. These results scale far beyond these small load tests and bring the SDK towards real-world performance improvements as demonstrated by the Cronos team.
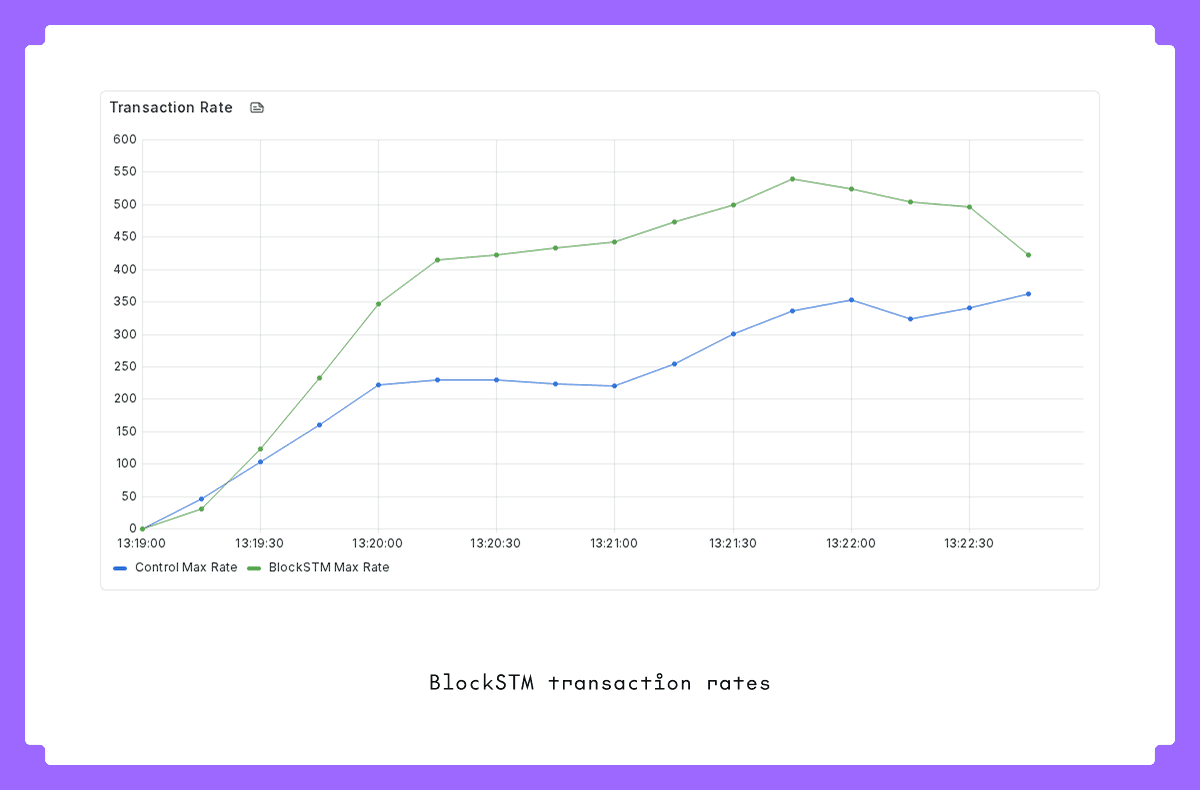
Storage Layer - IAVL Rewrite:
A complete rewrite of the IAVL library for the Cosmos SDK store is underway. Current benchmarks are showing write improvements up to 30x faster than IAVL v1. This project targets three areas simultaneously: execution speed, scalability, and tuning for different node types, including archive nodes.
IAVLX (current working name) is inspired by both Binary Builders’ prior IAVL V2 and Crypto Org’s MEMIAVL. IAVLX combines IAVL V2's efficient memory handling at scale with MEMIAVL's fast query performance, while solving both systems' disk management issues through a new incremental changeset design – these innovations would not have been possible without both these teams’ work.
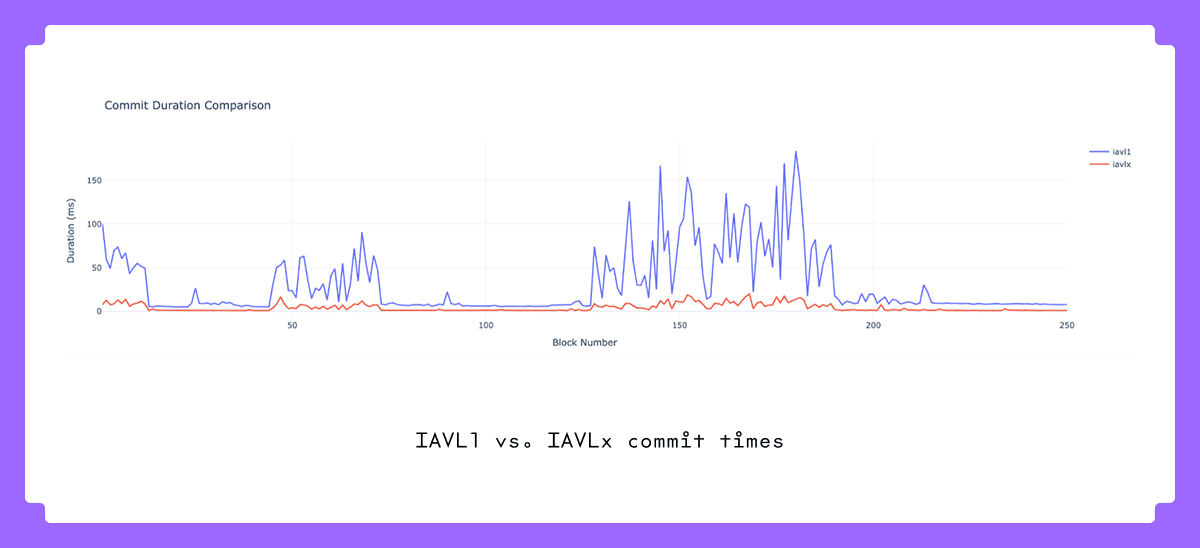
Reduced Commit Times:
IAVLX significantly reduces commit times, enabling faster block production—achieving around 20 ms compared to IAVL v1’s spikes of ~150 ms.
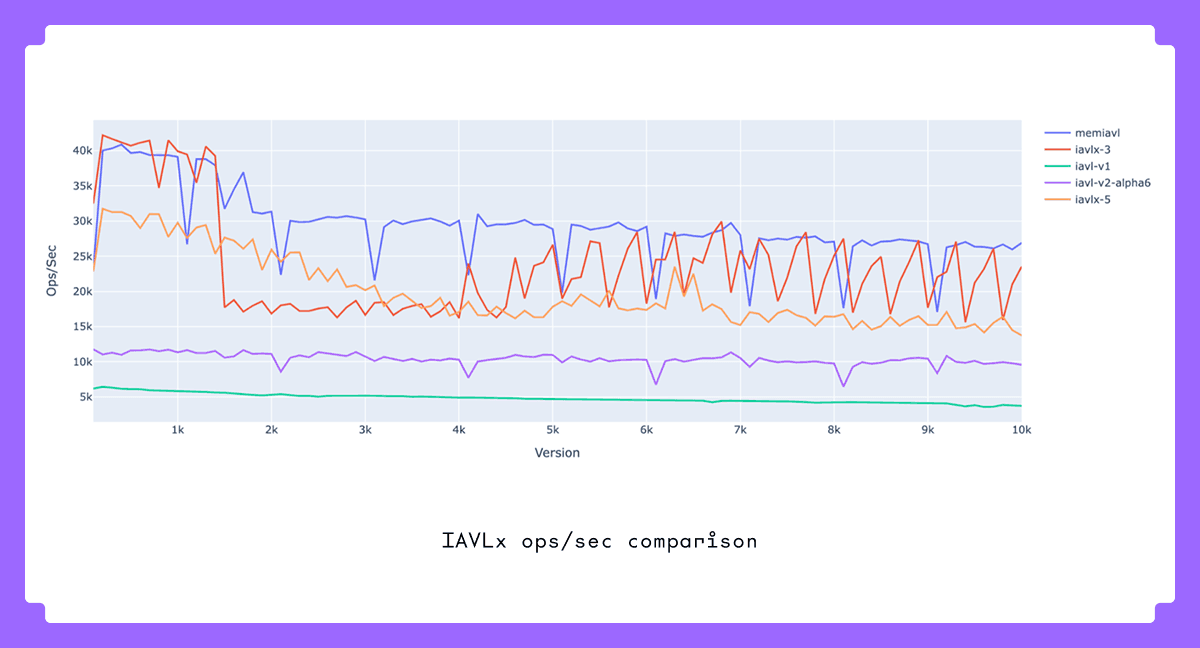
Improved Tree Performance:
IAVLX sustains roughly 25,000 ops/sec, compared to about 5,000 ops/sec in IAVL v1.
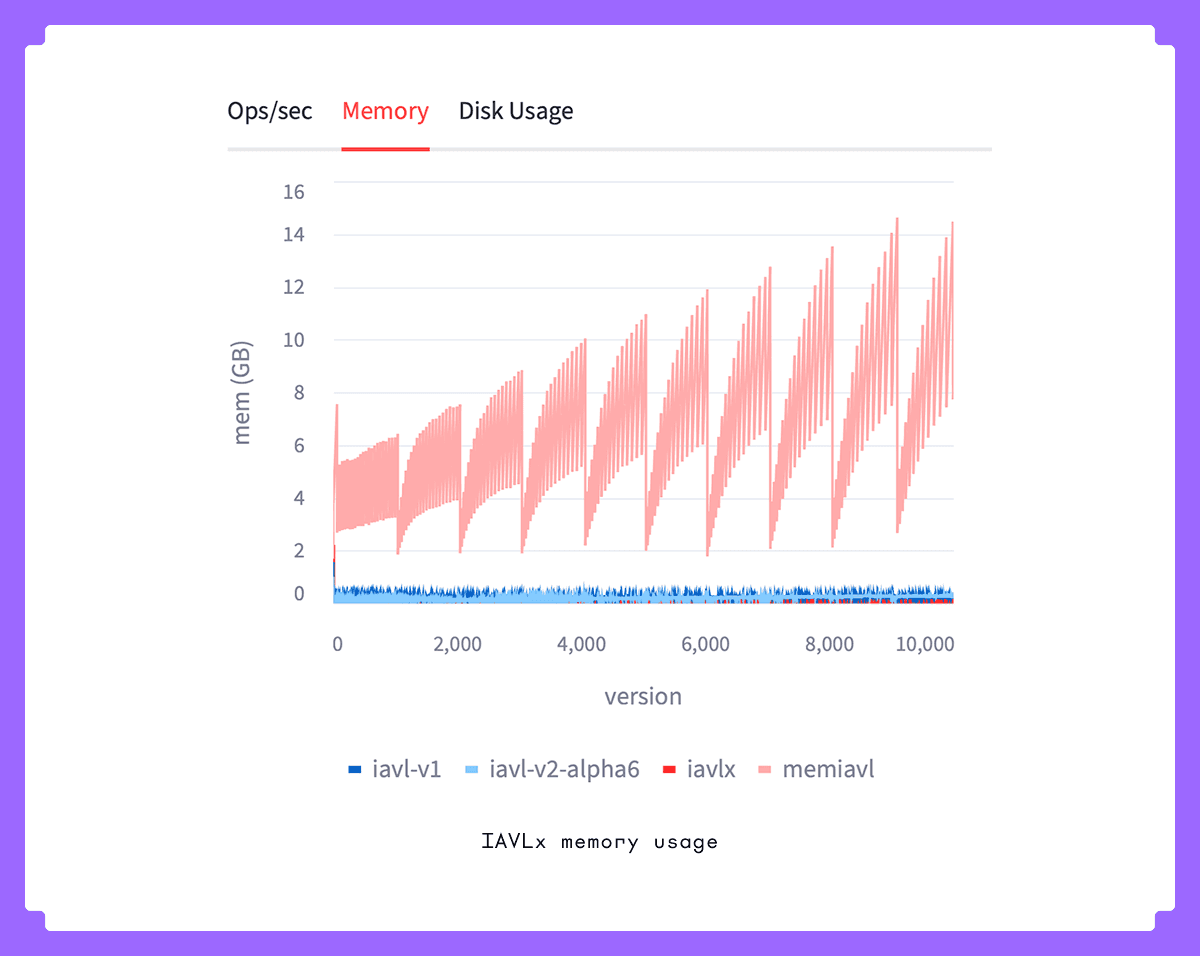
- Stable Memory Usage: IAVLX is able to keep memory pressure low, not exceeding 2GB while maintaining greatly improved performance.
- Changesets: IAVLX uses an optimized changeset architecture that stores only incremental modifications between tree versions, improving storage efficiency and reducing operational costs for node runners.
- Compaction: IAVLX treats pruning as a first-class concern and includes a configurable background compaction process that keeps the storage footprint efficiently bounded. Developers and node operators gain deep configurability over memory and storage usage, enabling trade-offs such as higher RAM consumption for faster reads and writes.
- Custom Storage Layout: Unlike IAVL v1, which used a generalized database that added overhead, IAVLX uses a custom storage layout optimized for Cosmos SDK workloads. The files are memory-mapped at runtime, enabling fast reads and writes.
CometBFT
At the consensus level, we are targeting optimizations initially around networking and ABCI Client lock contention that will allow CometBFT to improve in stability, latency, and concurrency.
- P2P Optimizations: Using libp2p, we’ve implemented an alternative P2P networking architecture that can fully replace Comet’s existing networking layer. It integrates seamlessly with the Reactor system, leaving consensus logic unchanged while improving message round-trip times and concurrent message processing.
The current ABCI client introduces overhead for high-throughput RPC workloads and lacks protections against transaction-spam-driven DoS. We’re actively improving both sides of the ABCI connection to eliminate these bottlenecks.
Connectivity

Connectivity has always been a core strength of the Cosmos Stack, with IBC, but the next generation of applications requires broader reach. Whether the other end is a Cosmos blockchain, a banking ledger, a payments network, an enterprise database, an SVM/EVM/ANYVM… IBC needs to connect.
To meet this demand, we are expanding the connectivity layer with modules like attestation, GMP, and IFT that make moving data and assets more simple, and flexible. Connecting over 200 public networks and dozens of private consortiums today, IBC is entering its next phase with:
IBC Attestor Light Clients:
The Attestor light client enables trust-minimized IBC connectivity for chains that lack native light client support – like Solana and EVM rollups. This approach provides a generic, multi-sig-based verification layer that can attest to any blockchain architecture without requiring custom light client implementations for each. The initial Go implementation is now available in ibc-go: cosmos/ibc-go#8717
Solana / EVM / L2 Support:
A major focus is extending first-class IBC connectivity to Solana. We’re delivering two light clients tailored for different use cases. The CometBFT light client enables trust-minimized transfers from Cosmos chains into Solana. Alongside it, a new Attestor light client supports updates from Cosmos, SVM, and EVM/L2 chains using an off-chain m-of-n attestation model. Both clients are being built with shared libraries across Solana, EVM, IBC-go, and WASM, and integrate directly with our Proof of API (or relayer API) to simplify relaying work.
IFT – Interchain Fungible Token:
We’re introducing a new fungible token standard designed for modern multichain applications. IFT uses a mint–burn model rather than ICS-20’s voucher system, eliminating path-dependent denoms and making asset behavior more predictable for developers and users. Initial implementations target Solana and EVM, with support for additional chains to follow.
GMP – General Message Passing:
While IBC handles arbitrary message transport, triggering contract execution on the destination chain requires more work. For that, we are building a generalized messaging layer that enables contracts and programs to trigger execution on other IBC-connected chains. This extends interoperability beyond asset transfers and supports more sophisticated cross-chain applications without requiring custom bridging logic.
Across all these initiatives, our goal is to make connectivity a reliable foundation for developers operating in a multichain world. We will share progress as components mature and work closely with ecosystem teams to validate assumptions, and refine UX for new emerging use-cases.
Enterprise Tools

Alternative methods of managing and permissioning validator sets have long been missing from the Cosmos Stack. Namely, a proof of authority system has been a long pursued goal, but has never managed to make it into the Cosmos SDK. This consensus option is key for enterprise customers, who more often decide to build permissioned networks with custom governance, validator, connectivity and access definitions.
Native Proof of Authority
Current solutions for proof of authority are brittle, require “hacking” the default proof of stake system, including governance and distribution, and add more complexity to an application than they need to. To address it, we have built native PoA into the stack.
We have developed an internal module (x/poa) designed to satisfy the following requirements:
- Provide a token-free alternative to x/staking for easy-to-configure PoA operation
- Offer a migration path from PoA to PoS
- Enable token-free governance by decoupling x/staking from the governance keeper
- Provide distribution functionality to authorized validators based on validator power
- Integrate with existing Cosmos SDK modules rather than reimplementing existing, battle-tested functionality
We are currently working on this module internally, and expect to upstream it to the Cosmos SDK once we have sufficiently trialed it and validated it against our requirements. The expected first release for this will be in H1 2026 alongside the release of Cosmos SDK v0.54.
Programmable Privacy
Programmable confidentiality and privacy are a key feature requirement for enterprises. While there are multiple approaches and solutions applicable to the Cosmos Stack, it is a priority for us to have a native, production-ready solution that offers programmable privacy that can more easily adapt to each enterprise’s environments/needs.
In 2025, we researched privacy technologies across TEE, ZK, and FHE approaches, in and out of the Cosmos ecosystem. What we found: TEEs have security concerns for persistent data, FHE remains impractical at scale, and while permissioned blockchains are the most production-ready today, and you can add permissioning systems to them, they are a light step to solving transaction-level privacy.
For 2026, we see ZK UTXO models as the most promising path to transaction-level privacy that meets regulatory requirements like selective disclosure and auditability. Our native Proof of Authority module, shipping 2026, is a key piece: once permissioning exists, ZK UTXO becomes practical for private payments between KYC'd parties. We're also exploring sidecar architectures using TEEs for computation outside consensus, and integrations with existing privacy solutions as a bridge. The goal is private transfers that work with the stack and particularly Cosmos EVM, so enterprises can build compliant financial applications more easily.
Developer Experience Improvements
We recognize that the current application upgrading, testing and development flows can be vastly improved in the Cosmos SDK. From our experience with releasing v0.53, we’ve learned that delivering a stable, non-breaking platform is just as important as pushing new features.
You want to know that you won’t be slowed down by code migrations and uncertainty just so you can access the latest features and performance improvements. We will continue developing our software with this in mind while we start to push more features forward.
Addressing Boilerplate While Doubling Down on Modularity:
We are not satisfied with the excessive boilerplate code and potential "footguns" (easily made mistakes) that developers currently encounter using the SDK. At the same time, modularity has been a key driver of adoption, and we intend to further enhance it by maintaining optionality while providing sensible default behaviors to reduce boilerplate.
Setting up a Cosmos SDK application has always required external tooling, copy-pasting and trial-and-error programming, even for experienced developers. In our future releases, we aim to deliver a minimal, simple, declarative system to setting up your app without sacrificing any of the customization that you have come to expect and benefit from.
Retracting CometBFT v1 and v2 and focusing development on v0.38:
Our commitment is to deliver stable, easily upgradable software. To achieve this, we are making strategic short-term decisions that will enable a faster cadence of high-quality releases. The v0.53 SDK release proved that fully non-breaking upgrades are achievable while still delivering meaningful features.
However, CometBFT v1 introduced major API-breaking changes, creating pain points for developers and causing downstream incompatibilities across the Cosmos SDK, IBC, relayers, and Interchain Security.
Due to the breaking changes in v1 and v2, we will not be pursuing further development on these versions. Instead, all new work and features will target CometBFT v0.38, which is the most widely-used version found in SDK v0.50 and v0.53 chains currently in production.
Features that were important to the community in CometBFT V1, such as performance optimizations and BLS signing, will be integrated into our next CometBFT release: v0.39.
Making upgrades easier for future releases across the entire Cosmos Stack:
In the event that future breaking changes become necessary in any stack component, we will provide tooling to automatically support code migrations and will always deprecate APIs one release before their removal, providing a clear migration path.
Relocation of a selection of Cosmos SDK Modules:
We will be relocating several existing SDK modules to a contrib folder within the codebase. This decision reflects our commitment to strong security guarantees and a focus on widely used features. By reducing our maintenance surface area, we can concentrate more on key improvements such as performance rather than primarily maintaining legacy modules.
This move means that:
- These modules are not covered by the official bug bounty program.
- They have not undergone the same level of scrutiny and security review as core modules.
- They are not considered "core" to the fundamental operation of an SDK chain.
Modules that will move to /contrib:
- x/nft (Non-Fungible Token module)
- x/group (Group module for multi-signature accounts)
- x/circuit (Circuit breaker module)
- x/crisis (Crisis module for detecting and halting abnormal states)
The code for these modules will remain in the repository for historical reference and for teams that continue to rely on them. We encourage anyone interested in their ongoing development to contribute, fork, or take on maintenance. Cosmos has always valued its open-source ecosystem, and this is an excellent opportunity for deeper involvement.
Upcoming Planned Releases for the Cosmos Stack

We are excited to announce upcoming releases of the Cosmos Stack core software, including CometBFT, Cosmos SDK, IBC, and Cosmos EVM! With these new releases, we are executing on our plan of delivering and maintaining release families, meaning that we will guarantee support and compatibility from day one. Our aim with this approach is to minimize friction for developers and provide a much clearer picture for how to compose your own applications.
CometBFT v0.39 Release:
We will release v0.39 with an easy upgrade path for all SDK users. This release will include:
- BLS (Boneh–Lynn–Shacham) signing for enhanced security and efficiency.
- Critical bug fixes.
- Experimental libp2p networking with Quic
Cosmos SDK v0.54 Release:
This version will feature an easy upgrade path via a code migration tool. The release will include:
- Support for CometBFT v0.39.
- BLS signing capabilities.
- Bug fixes.
- BlockSTM integration.
- IAVL upgrades for improved data structures.
- Native Proof of Authority (PoA) support.
Upcoming Cosmos EVM Improvements and Features:
Ongoing Cosmos EVM efforts will focus on:
- Additional App wiring improvements.
- Continuous support for the latest Ethereum RPCs and EIPs.
- Performance improvements in the JSON-RPC layer.
Ibc-go v11 Release and Accompanying Software:
This release will focus on compatibility with the release family as well as enabling new composable ways to move tokens and data cross-chain.
- Support for CometBFT v0.39
- Support for Cosmos SDK 0.54
- GMP support
- IFT support
Security

Security remains a core priority for the Cosmos Stack, particularly as enterprise adoption continues to grow. As part of our stewardship of the stack, Cosmos Labs has taken ownership of the Cosmos bug bounty program, reinforcing our commitment to long-term security of the ecosystem at large.
Since assuming responsibility for the program, we’ve focused on improving responsiveness, expanding coverage, and clarifying security processes for researchers and ecosystem teams. This includes extending official bug bounty coverage to new components such as the Cosmos EVM, reflecting its increasing role within the Stack.
Bug Bounty Program Snapshot:
- $465,000 in total bounty payouts
- 24 confirmed vulnerability submissions
Security Policy:
We’ve published a unified security policy that outlines reporting guidelines, disclosure expectations, and response processes across supported Cosmos Stack components.
We encourage all security researchers and ecosystem teams to follow this policy and engage through responsible disclosure as we continue to expand security coverage alongside new releases.
To our Contributors: Thank You and Happy 2026!
We’ve significantly benefited from collaborations with teams like MANTRA, Cronos, and B-Harvest, who have made core contributions, such as major EVM features like EIP-7702—and are helping us upstream BlockSTM to the Cosmos SDK.
We’d also like to thank teams such as Binary Builders and Informal Systems, whose extensive work on the Cosmos SDK and CometBFT has pushed the technology forward. We deeply value these partnerships and look forward to working with even more teams across the ecosystem. Together, we can build an even more open and performant Cosmos Stack.
As we begin 2026 and leave 2025 behind, we want to acknowledge the teams, partners, and contributors across the Cosmos ecosystem whose work and trust make this stack viable in production today. Last year included major releases and deployments from teams such as Ripple, Ondo, Figure, and Stable, alongside many others building on Cosmos across banking, finance, government, enterprise, and blockchain.
Looking ahead, our focus is on scaling the infrastructure these deployments already rely on, so Cosmos continues to be a trusted, long-term stack of choice for critical systems well into the future.
Join our slack channel for tech-contributors, and visit our Github to follow new releases.
Stay connected
We are Cosmos Labs: building the infrastructure and solutions that power enterprise-grade technology and growth initiatives for Cosmos. Get in touch to speak with an expert about your company’s blockchain solution. Connect with Cosmos Labs on our website, X, and LinkedIn.